Salicylates Avoidance and Tinnitus
What are SALICYLATES?
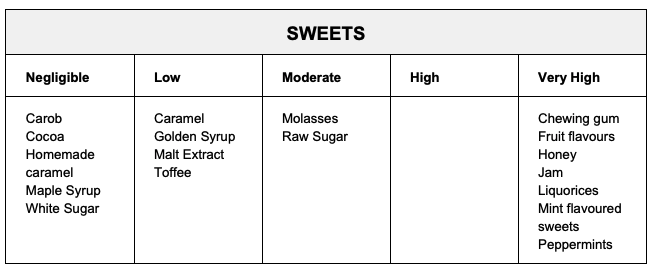
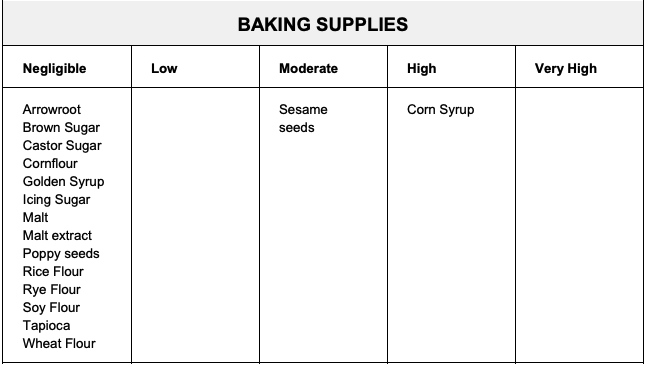
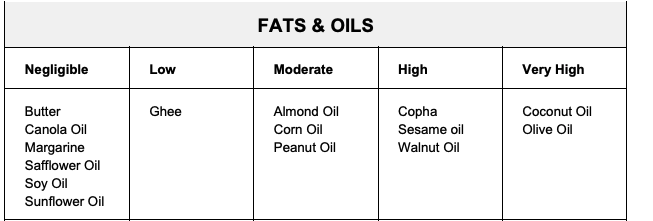
SENSITIVITY FOOD GUIDE BELOW
Current Studies
Salicylates are chemicals that occur naturally in many plants, including many fruits vegetables, herbs, spices, teas, seeds, flowers, and bark. Salicylates in plants act as a natural immune hormone and preservative, protecting the plants against diseases, insects, pests, fungi, and harmful bacteria. Salicylates are natural regulators of growth, flowering, ripening, and aging. Higher quantities of salicylates are found in firm unripe fruit and lowest when ripe fruit is ready to drop off the plant. Salicylates exist mainly in the skin zone (skin and just under the skin) and are concentrated by processing as in fruit or vegetable juices, sauces, pastes, powders, jams, syrups, and flavorings. Salicylates are also created synthetically and can be found in many medicines (ie. aspirin), perfumes, preservatives, industrial chemicals, plastics, and some pesticides. WHAT ARE SOME OF THE SYMPTOMS OF SALICYLATE SENSITIVITY? headaches or migraines itchy skin rashes such as hives (urticaria), eczema, and others irritable bowel symptoms – reflux in babies or adults, nausea, vomiting, stomach bloating and discomfort, wind, diarrhea and/or constipation bedwetting, cystitis asthma, stuffy or runny nose, nasal polyps, frequent throat clearing conjunctivitis behavior problems such as irritability, restlessness, inattention, oppositional defiance, symptoms of ADHD sleep disturbance - difficulty falling asleep, night terrors, frequent night waking, sleep apnoea, insomnia anxiety, depression, panic attacks rapid heartbeat and arrhythmias, tinnitus, hearing loss joint pain, arthritis, and more
This Graph from Study Linked above depicts increased Tinntius after Post Salicylate. “Following systemic salicylate treatment, the frequency tunings of tracked multiunits shifted maximal frequency sensitivities toward the 10–20 kHz frequency region, near the estimated tinnitus pitch.” Please see Stolzberg et al., 2011 for population statistics. [From Stolzberg et al. (2011) with permission].
From the Study - “Salicylate, the active component of the common drug aspirin, has mild analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory effects at moderate doses. At higher doses, however, salicylate temporarily induces moderate hearing loss and the perception of a high-pitch ringing in humans and animals. This phantom perception of sound known as tinnitus is qualitatively similar to the persistent subjective tinnitus induced by high-level noise exposure, ototoxic drugs, or aging, which affects ∼14% of the general population. For over a quarter century, auditory scientists have used the salicylate toxicity model to investigate candidate biochemical and neurophysiological mechanisms underlying phantom sound perception. In this review, we summarize some of the intriguing biochemical and physiological effects associated with salicylate-induced tinnitus, some of which occur in the periphery and others in the central nervous system. The relevance and general utility of the salicylate toxicity model in understanding phantom sound perception in general are discussed.”
Creds
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22557950/
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnsys.2012.00028/full
SENSITIVITY FOOD GUIDE - Click New Areas Below Big Image